Dementia is a term used to describe a group of symptoms that affect a person's ability to think, remember, and communicate. Dementia affects people of all ages but is most common in older adults. Dementia can lead to a decline in physical abilities and mobility. Dementia can also increase the risk of falls and injuries.
Essentially, dementia is a brain disorder that affects memory, thinking, and behavior. It is caused by diseases or injuries that affect the brain. Dementia may also be caused by a combination of factors, including changes in the blood vessels and the shrinking of the brain. Symptoms vary depending on the type of dementia.
What are the Symptoms of Dementia?
A primary symptom of dementia is memory loss. This usually includes forgetting crucial information like people's names, important dates, and events. Thinking and problem-solving skills may also decline. People with dementia often have difficulty completing regular tasks or making decisions. They may also become confused quickly or lose their sense of place. Behavioral changes can also occur, such as mood swings, agitation, or aggression.
How is Dementia Diagnosed?
Dementia can be challenging to diagnose because its symptoms overlap with other conditions. No one test can determine whether a person has dementia. Doctors typically use a combination of tests and clinical observations to make a diagnosis.
One standard test used to diagnose dementia is the mental status examination (MSE), which includes questions about a person's memory, orientation, language abilities, and ability to reason and problem solve. The doctor will also ask about the person's mood and behavior. Other tests that may be used include blood tests, brain imaging scans (such as MRI or CT scans), and neuropsychological testing.
What is the Treatment for Dementia?
- Managing medications and other treatments: It is essential to work with a doctor to ensure that all medications prescribed are appropriate for someone with dementia and that any treatments or therapies being used are effective and safe.
- Encouraging social and recreational activities: People with dementia may benefit from participating in social activities, and recreational pursuits, which can help keep them mentally stimulated and engaged.
- Providing support and assistance with everyday tasks: People with dementia may need help with tasks such as bathing, dressing, and grooming.
How Can I Help a Loved One with Dementia?
There are many ways to help a loved one who is living with dementia. You can help by creating a supportive environment at home, promoting independence, and providing assistance with activities of daily living as needed.
If they become agitated or confused, try to remain calm and reassuring. You may also need to adjust your lifestyle to better care for your loved one.

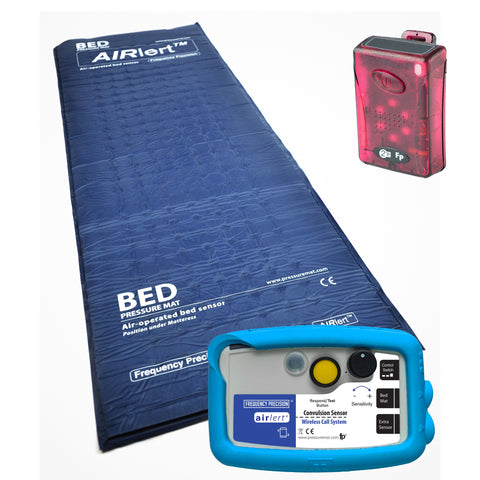
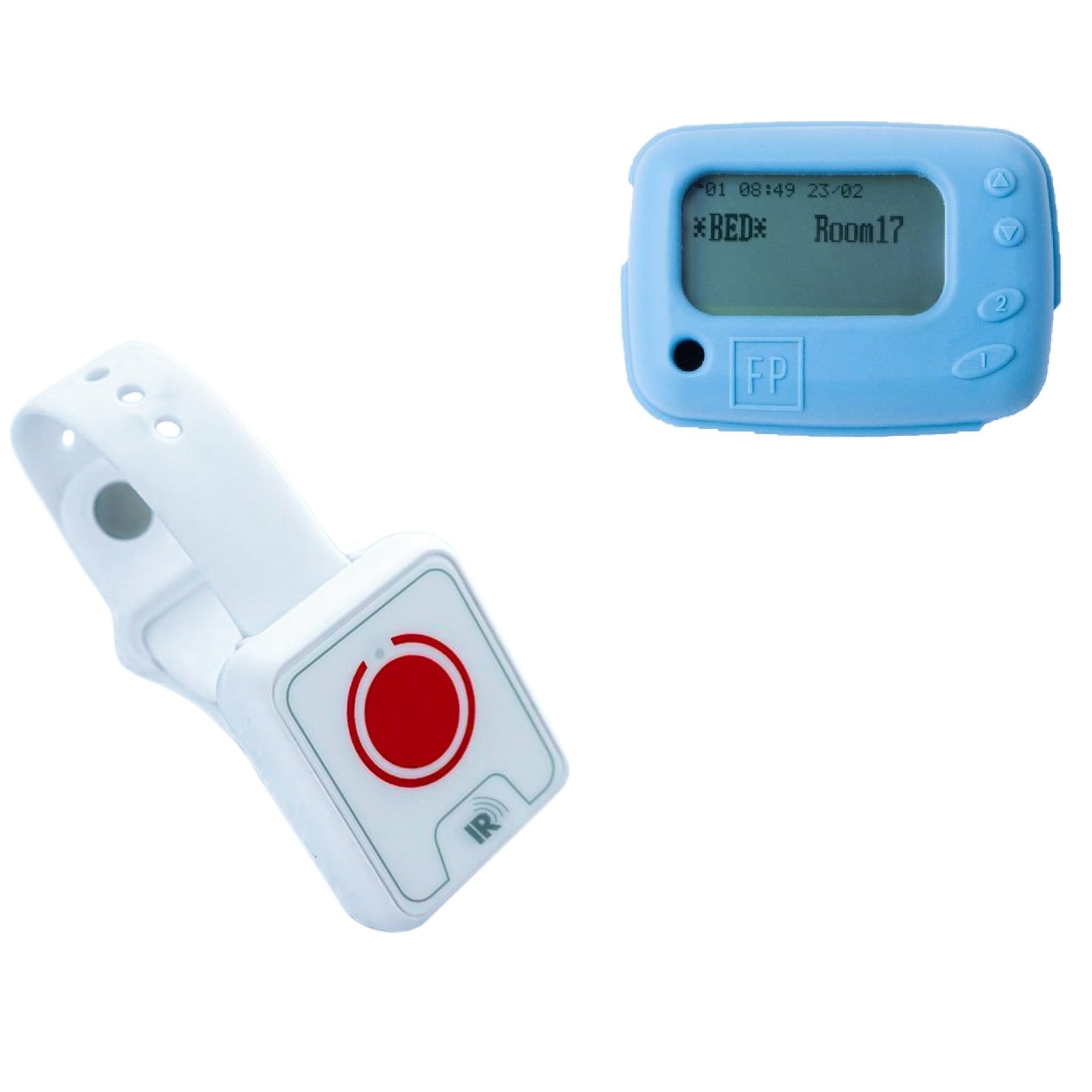
Frequency Precision offers nurse call systems and wireless door sensors that can help caregivers keep track of those with dementia, allowing them to provide assistance when it is needed most. The nurse call system allows the patient to reach out for help quickly in case of an emergency. The wireless door sensors can be installed on any door in the home and will send an alert to caregivers when the door is opened unexpectedly.
Contact us today for more information.